- Follow these steps to install the Arduino software on your Mac: 1 Go to the Arduino downloads page and click the Mac OS X link to download a.zip file containing a copy of the Arduino application for Mac OS X. Currently, the file is 71.1MB. That’s quite a large file, so it may take a while to download.
- 1 Go to the Arduino downloads page and click the Mac OS X link to download a.zip file containing a copy of the Arduino application for Mac OS X. Currently, the file is 71.1MB. That’s quite a large file, so it may take a while to download.
- May 16, 2020 If you are on the latest Mac OS you must use Arduino 1.8.12 or higher due to 64bit application enforcement that Apple put in place. Installation Instructions: Download the latest firmware pack that contains the latest Mac Arduino IDE and the TH3D Arduino Library Files from here: TH3D Unified Firmware Package.
- Follow this guide to install and learn about the Arduino IDE.
- Arduino Ide Mac Download Mac
- Arduino Ide Mac Download Softonic
- Arduino Ide Mac Download App
- Arduino 1.0.6
Follow these steps to install the Arduino software on your Mac: 1 Go to the Arduino downloads page and click the Mac OS X link to download a.zip file containing a copy of the Arduino application for Mac OS X. Currently, the file is 71.1MB. That’s quite a large file, so it may take a while to download.
Jan 22, 2019 By Team YoungWonks *
How do you program an Arduino using a Mac? This blog will tell how. But before we get into that, let’s take a look at what is an Arduino?
What is Arduino?
An Arduino is basically a single board microcontroller that is used for building digital devices and interactive objects that can sense and control objects in the physical and digital world. These Arduino boards are available both in preassembled form or as do-it-yourself (DIY) kits. Arduino board designs use a variety of microprocessors and controllers. The boards come fitted with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that can be interfaced to several expansion boards or breadboards (shields) and other circuits.
One of the biggest advantages that Arduino boards have over Raspberry Pi is the fact that they can read sensitive values from sensors and Arduino boards have analog input and output and not digital input output which is the case with Raspberry Pi. This is why in some instances - especially where exact values are needed - it is a more apt choice. Say, if you want to make a device that automatically waters your plants. Now to do this, you have to measure the exact soil moisture, so an Arduino is a better bet because it can read analog values as opposed to the Raspberry Pi which will need another chip to read analog values.
Arduino has low maintenance and doesn’t get disrupted by power outages. But image processing needs can be done better with Raspberry Pi and Pi camera.
In this blog, we shall look at how we can program an Arduino board using a Mac OS. Here’s the step-by-step process to program an Arduino board with a Mac:
Downloading and installing Arduino on a Mac
Step 1: Get all the needed equipment in place. This means having with you the Arduino Uno board and the USB data cable that will help you connect the board to your Mac.
You’ll also need a breadboard, jumper cables(M-M), an LED and a resistor (with a resistance of say, 330 Ohms).
Step 2: Then start by connecting the narrow end of the USB data cable to your Arduino board as shown below.
Step 3: Then connect the other end of the USB data cable to your Mac. At this stage, your Mac and the Arduino board have been connected to each other using the USB cable. Refer to the pic below.
Step 4: Now go on to download the Arduino IDE on your Mac. To do this, open Safari on your Mac and just go to the website www.arduino.cc. Once you have opened the website, go to the software section and click on downloads from the dropdown menu. Now select the Mac OS X version, hit download and wait for the download to finish. Once it downloads, one can run the Installer in the next step.
Step 5: To install the IDE, we need to run the file that we just downloaded. Click on Agree and continue with the default settings for the rest of the installation. Once the installation is done, click on the close button to finish the installation.
Now that we have downloaded and installed the Arduino IDE on our Mac, we can carry out a number of tasks using the Arduino IDE. This includes getting the board to say, “Hello World”, running the counter program and lighting an LED - all using the Arduino.
Saying “Hello World”
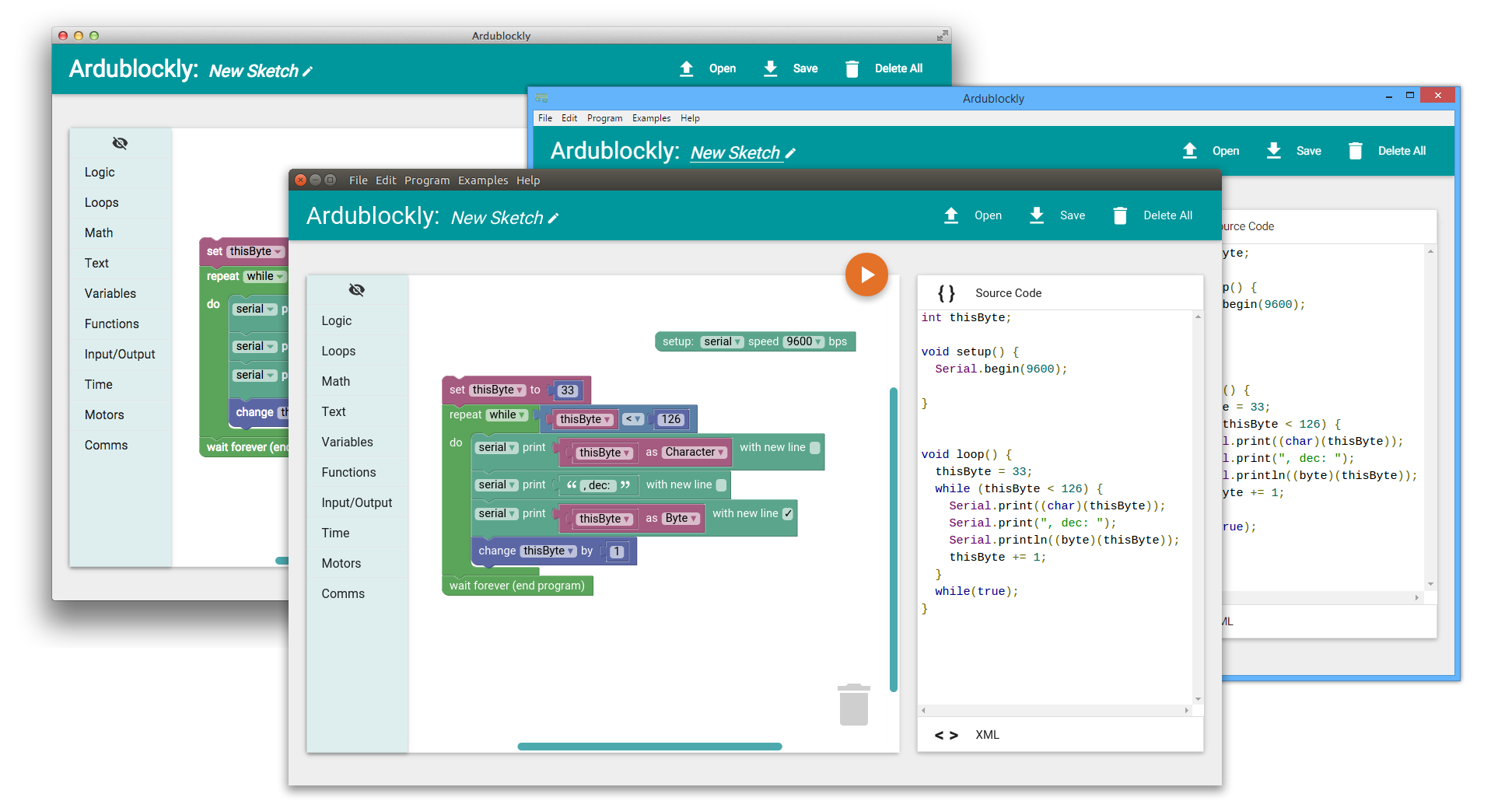
Let’s look at what goes into writing our first program, the “Hello World” program. Let’s open the Arduino IDE that we have installed on the Mac. Make sure you check the board name under the Tools option as Arduino Uno. Also make sure that the communication port is selected as COM3. Now to see the information sent by our Arduino, we have to open the serial monitor we see on the right.
In the program, we start by putting Serial.begin 9600 in the void setup function which is the one-time setup required for exchanging information over the serial port from the Arduino to the computer. 9600 here is called the baud rate. It is the rate at which the Arduino can send symbols or characters to the computer.
In the void loop function, we use a very simple serial.print to show data on the serial monitor.
You can first save it and then upload the design onto the Arduino. You’ll then see that the words “Hello World!” are being sent by the Arduino to the computer and we can see the words on the serial monitor. You’ll see that the words “Hello” and “World” are appearing next to each other. However, if we use a n in our print command, we will see the two words printed one below the other.
Arduino Ide Mac Download Mac
Running the Counter Program
Let’s take a look at the next program. We will design a simple counter by opening the Arduino IDE and the serial monitor. Let’s start by defining the counter variable. Here we say int <space> counter equals one and add a semicolon at the end. This initializes the value of the counter to 1 at the beginning. Now just like in the previous program, we initialize the serial connection.
In the loop, we print the counter value and we also increase the value of the count by one. Here, we use the printIn function to automatically add a new line after having printed the value of the counter. Now this would be too fast and for us to understand what’s happening in the output, we add a delay and the argument is in milliseconds. So for a one second delay, we provide an argument of thousand to the delay function. Finally, increase the value of counter by one using the counter++ statement. Once we save and upload this design onto the Arduino, we will be able to see that a counter variable is constantly being increased in value and this value is being communicated to the computer over the serial connection.
Lighting an LED
Lighting the inbuilt LED on the Arduino
Now the next program we will be working on is blinking the Arduino’s inbuilt LED. You can see that right next to pin number 13 among the digital pins, there’s an LED which is orange in colour. We will learn how to make it blink once every second. And just like we do with the Raspberry Pi, we will start by initializing the pin to be an output so we can control its values. Here we say pinMode and we say 13 which is the pin for the inbuilt LED and we set it as an output so that we can send values of high or low. We then begin our loop function by setting value of the 13 pin to 1 (or high). We do this by using the DigitalWrite function. We then add a delay of one second and then we set the value of the 13 pin as low. Don’t forget to add a delay after turning it low. Now when you run the code, you should be able to see the light next to the pin number 13 blink.
Writing the program to blink an LED on the breadboard
Here we will see how one can write the program that allows the Arduino to make an LED on the breadboard blink once every one second. Just like in the previous case, we will set values and this time, we will choose pin number 12 and we will set it as an output. So we type the pinMode, 12, output. In the void loop, we use the serial to communicate messages from the Arduino to the computer. We use the DigitalWrite function to turn the pin on or set it to high. Then we add the delay of one second. In the same fashion, we will turn the pin off by using the DigitalWrite function. Similarly, we can add a message and a delay so that we see the output very clearly.

Next you can save and upload this. Go to your Arduino, make sure you have the serial monitor open so you can see the output. Now this code seems to work as it prints LED high and LED low every one second. At this stage, we need to make an LED circuit on the breadboard and connect it to the Arduino to see the actual result.
Making connections to blink an LED on the breadboard
Now we will explore the connections to be made on the breadboard so as to make an LED blink from the Arduino.
Here’s how you make connections to blink an LED on the breadboard using an Arduino:
Just like with Raspberry Pi, we set up the LED first. We place the LED on the breadboard across the middle separation.
Then we add a resistor (say with a resistance in the range of 220 to 600 ohms). We place one end of the resistor on the same line as the LED.
Now we connect the resistor’s other end to the railing for the Ground.
We use a wire to connect it to the Ground pin on the Arduino.
The closeup of the Arduino after the connections have been made will look like this.
We then connect the other end of the LED to the pin number 12 which we are programming for.
The closeup of the breadboard after the connections have been made will look like this.
Since the program is already on the Arduino, we should immediately be able to see the light blink.
Here's a video explaining in entirety how to program an Arduino using a Mac:
*Contributors: Written by Vidya Prabhu; Lead image by: Leonel Cruz
Arduino Ide Mac Download Softonic
The Arduino Integrated Development Environment (Arduino IDE) is the free software required to interact with your Arduino controller board, without the Arduino IDE you can’t program your Arduino microcontroller to do cool stuff like control a cool robot car.

Choose a device to install the Arduino IDE software on, in the example below I’ll be installing the software on a Desktop PC running Windows 7.
Download the Arduino IDE Software
Go to the Arduino IDE Download webpage & download the relevant version for your device.
The Arduino IDE software is available for Windows, Mac and Linux operating systems.
Since I’m installing on a Desktop PC running Windows 7 I downloaded the Windows Installer, for Windows XP and up with filename: arduino-1.8.5-windows.exe.
Install the Arduino IDE Software
Install the Arduino IDE software by running the downloaded file and follow the instructions. Installing the IDE software is like installing any software on a PC, lots of mouse clicking :-)
Read the Arduino License agreement and click the “I Agree” button.
Unless you have a reason to change them, keep all the Arduino IDE software components ticked and click the “Next” button.
On the next window you can choose to change the folder where the Arduino IDE software is installed, or keep the default location and click the “Install” button.
The Arduino software will start to install.
This can take sometime and you’ll be presented with various drivers to install including Arduino USB drivers and COM/LPT port drivers, I suggest you install them all.
When complete the Arduino IDE Software is ready to run.
Running the Arduino IDE Software
Attach your Arduino Microcontroller board (I’m working with an Arduino UNO clone) to your device with a USB cable.
After connecting the Arduino UNO via USB to a Desktop PC, the power light on the Arduino UNO will light up (the USB cable powers the UNO board, no need for a power supply) and you should get a “Found New Hardware” message from Windows.
Windows will attempt to install the Arduino Driver Software. Some Arduino tutorials recommend canceling Windows automatically installing the Arduino driver software and installing manually via the Device Manager. No idea why they recommend making the process more difficult?
It took a while for Windows to install the driver for my UNO, but everything worked perfectly first time and the Arduino UNO was installed on COM4.
Arduino Ide Mac Download App
We are almost done.
Select the Correct COM Port
Although Windows has successfully installed the Arduino on COM4 (could be COM3 or another port) the Arduino IDE Software doesn’t automatically select the relevant serial port.
Arduino 1.0.6
To select the correct port click “Tools”, hoverover ‘Port:”COM4 Arduino Genuino UNO”‘ and click “COM4 Arduino Genuino UNO”.
That’s it, you’ve successfully installed the Arduino IDE Software.
Feel free to confirm everything is setup correctly by going to “Tools” > “Get Board Info”.
The “Get Board Info” pop up will list information about your Arduino microcontroller board.
The board info above shows it’s an Arduino/Genuino UNO which in simple terms means it’s an Arduino UNO.
